Understanding executive function is crucial in managing ADHD. It’s a set of mental skills that help us get things done. But what happens when these skills are impaired? ADHD often affects executive function, leading to challenges in daily life. This can impact academic, professional, and social settings. Fortunately, there are strategies to improve executive function. From behavioral therapies to medication, and even the help of an ADHD executive function coach.
This guide will delve into the importance of executive function in ADHD management. It will provide insights into finding a coach, using an ADHD executive function chart, and more.
What is Executive Function?
Executive function refers to a group of cognitive processes. These are essential for managing daily life tasks. They include skills such as working memory, flexible thinking, and self-control.
These mental skills are needed for planning, focusing attention, and remembering instructions. They are vital for organizing and completing tasks efficiently.
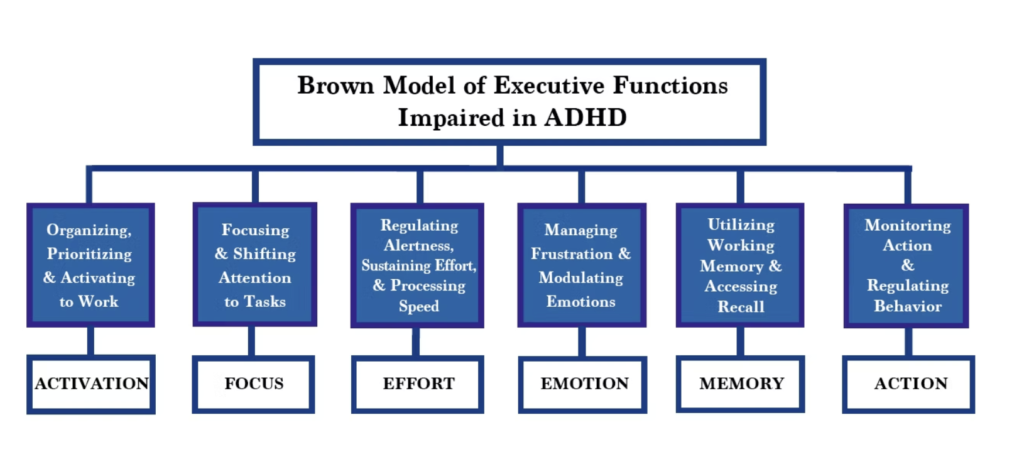
To better understand, consider this list of primary executive function skills:
- Working Memory: Holding information in mind and using it.
- Cognitive Flexibility: Adapting to new situations or rules.
- Inhibitory Control: Resisting impulses and staying focused.
These skills develop throughout childhood and adolescence. They help individuals manage time, solve problems, and regulate behavior.
Executive function acts like the brain’s “control tower.” It guides us through complex and simple tasks alike.
When functioning well, executive skills allow people to multitask and set goals. Good executive function enhances overall productivity and effectiveness in everyday life.
How ADHD Affects Executive Function
ADHD, or Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, significantly impacts executive function. Individuals with ADHD often face challenges in organizing tasks and managing their time effectively. These difficulties stem from disruptions in the brain’s executive functions.
One of the primary issues is with working memory. Those with ADHD may struggle to hold important information in mind while performing tasks. This can lead to difficulties in following multi-step instructions or completing complex projects.
Additionally, ADHD can hinder cognitive flexibility. Individuals might find it hard to switch focus from one activity to another. This rigidity can make it tough to adjust to new information or modify strategies when things aren’t working.
Inhibitory control is another affected area. People with ADHD frequently grapple with impulsivity, acting without fully considering the consequences. This can lead to problems in academic, professional, and social contexts, where thoughtful decision-making is crucial.
Understanding these executive function challenges is vital. It helps in developing targeted strategies to support those with ADHD in their daily lives. Emphasizing this connection can guide better interventions and improve management efforts for individuals struggling with ADHD.
Common Executive Function Challenges in ADHD
People with ADHD face unique challenges that affect their executive function abilities. These difficulties can vary widely between individuals but share some common elements that complicate everyday tasks and responsibilities.
For many, task initiation proves problematic. Initiating a task can require more effort and planning than it does for others. This often results in procrastination, delays, and feelings of being overwhelmed.
Another significant challenge lies in emotional regulation. Those with ADHD may experience strong emotional reactions and have difficulty managing them. This can affect relationships, as impulsive responses might lead to misunderstandings or conflicts.
Some typical executive function challenges in ADHD include:
- Difficulties in planning and organizing.
- Poor time management and frequent lateness.
- Trouble setting and achieving goals.
- Struggles with keeping track of personal belongings.
- Hardship with maintaining focus and attention.
These challenges impact various life areas such as academics, work, and social interactions. Recognizing these obstacles is the first step in developing effective strategies to manage them. Understanding these common challenges provides a foundation for building tailored approaches to improve the quality of life for those with ADHD.
Strategies for Improving Executive Function
Managing executive function deficits in ADHD involves using a variety of strategies. These approaches can help enhance planning, organization, and task management skills. Tailoring these strategies to individual needs is crucial for success.
One effective method is creating routines. Routines provide structure and predictability, which can help improve focus and task completion. Consistent daily habits can make a significant difference.
Developing skills in goal setting is equally vital. Setting clear and achievable goals can provide direction and motivation. It can also help break larger tasks into manageable steps.
Some helpful strategies to consider include:
- Establishing clear, simple routines.
- Using visual aids like calendars and to-do lists.
- Breaking down tasks into smaller, actionable steps.
- Setting specific, realistic goals with time frames.
- Practicing mindfulness to improve focus and emotional control.
By employing these strategies, individuals with ADHD can start seeing improvements in their executive function skills. This not only boosts productivity but also enhances personal growth and well-being.
Behavioral Therapies and Interventions
Behavioral therapies can be a beneficial component in managing ADHD. These therapies focus on modifying actions to improve executive function skills, addressing behaviors that hinder success. Through structured techniques, individuals learn how to manage challenges effectively.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely used in ADHD management. It helps identify unhelpful thinking patterns and replaces them with positive strategies. CBT can enhance emotional regulation and improve focus, reducing impulsive actions.
Interventions often include social skills training. This type of training helps improve interaction abilities and emotional understanding. Developing better social skills can foster more positive relationships and reduce social anxiety. By integrating these therapies and interventions into daily life, those with ADHD can better manage their executive function difficulties.
Using Medication to Optimize Your Brain
Medication can play a crucial role in managing executive function deficits in individuals with ADHD. Certain medications help improve focus, attention, and impulse control, allowing better management of daily tasks.
Stimulant medications are commonly prescribed for ADHD treatment. These medications can significantly enhance executive function by increasing neurotransmitter activity in the brain. Some non-stimulant options are also available, offering benefits for those who may not respond well to stimulants.
However, medication should be part of a comprehensive treatment plan. It is essential to combine it with strategies like behavioral therapy or coaching to achieve the best outcomes. A healthcare provider can help determine the most suitable medication strategy for each individual.
The Role of ADHD Coaches
ADHD executive function coaches provide valuable support for those struggling with executive function deficits. They work one-on-one with individuals to develop personalized strategies that address specific challenges. Through coaching, clients learn how to manage time, organize tasks, and set realistic goals.
Coaching involves building self-awareness, helping clients identify their strengths and weaknesses. This self-awareness forms the foundation for developing effective coping strategies. Coaches also offer accountability, encouraging clients to follow through with their plans.
An ADHD executive function coach can be instrumental for children and adults alike. For parents seeking to support their children, they provide guidance on managing daily routines. Adults can benefit by learning skills that improve professional performance and personal relationships. Engaging with an ADHD coach can lead to significant improvements in executive function abilities, enhancing overall quality of life.
Finding an ADHD Executive Function Coach Near Me
Locating a qualified ADHD executive function coach in your area can make a significant difference in managing ADHD challenges. Start by searching online directories specific to ADHD coaching. Websites like the ADHD Coaches Organization can connect you with certified professionals.
It’s also helpful to ask for recommendations from healthcare providers, therapists, or local support groups. Personal referrals can lead you to reputable coaches experienced in working with ADHD individuals. Contact potential coaches for consultations to discuss their approach and see if they fit your needs. The right coach can guide you in improving your executive function skills and overall well-being.
Utilizing an ADHD Executive Function Chart
An ADHD executive function chart can be a valuable tool for tracking progress and identifying areas for improvement. These charts break down complex tasks into manageable steps, making it easier to tackle daily responsibilities.
By visually organizing tasks and goals, individuals can enhance their focus and clarity. Parents and educators can use these charts to support children in developing better habits. Regularly updating and reviewing the chart helps maintain motivation and encourages consistent effort toward building executive function skills. This tool promotes self-awareness and supports effective ADHD management.
Supporting Executive Function Development in Children
Cultivating executive function skills in children with ADHD is crucial for their growth. Support from parents and educators can make a significant difference. Establishing routines and providing clear expectations can assist children in managing their tasks more effectively.
Activities that promote planning, organization, and emotional regulation can enhance executive function. Games that involve strategic thinking or simple memory exercises can be both educational and fun. Tailored approaches that match the child’s interests can encourage engagement and willingness to learn.
Open communication between children and adults is vital. Understanding each child’s unique needs helps in developing personalized strategies. Celebrating small achievements can boost a child’s confidence and inspire them to keep improving. Consistent support fosters a nurturing environment where children can thrive, gradually strengthening their executive function skills.
The Importance of Routine and Structure
For individuals with ADHD, routine and structure provide a reliable framework. This consistency can reduce stress and increase efficiency in managing daily tasks. It helps minimize chaos, which can sometimes overwhelm those with ADHD.
Establishing clear routines can aid in developing discipline and predictability. Scheduled times for various activities, like homework or chores, promote better time management. This structured approach not only boosts productivity but also enhances executive function by creating a stable environment where individuals can focus and thrive.
Technology and Tools to Assist with Executive Function
Technology offers valuable support for managing executive function in ADHD. Tools like organizational apps and reminders help individuals stay on track with tasks. These digital aids provide prompts for appointments, deadlines, and routines.
Apps designed for ADHD can improve focus and productivity. They offer features such as timers and checklists to break tasks into manageable parts. Utilizing these tools can lessen the cognitive load and help maintain attention on the task at hand, leading to improved executive function skills over time.
Conclusion: Embracing a Holistic Approach to ADHD Management
Managing ADHD effectively requires a comprehensive approach that addresses various aspects of daily life. By understanding the role of executive function, individuals can better implement strategies for improvement. Embracing techniques from behavioral therapies to technological tools provides a well-rounded support system.
Fostering an environment that encourages routine and structure is crucial. Involving coaches, educators, and family creates a network of support, enhancing the overall quality of life. By combining multiple interventions, those with ADHD can develop the necessary skills to manage their symptoms and thrive in personal and professional spheres. This holistic approach is essential for long-term success.


Leave a Reply